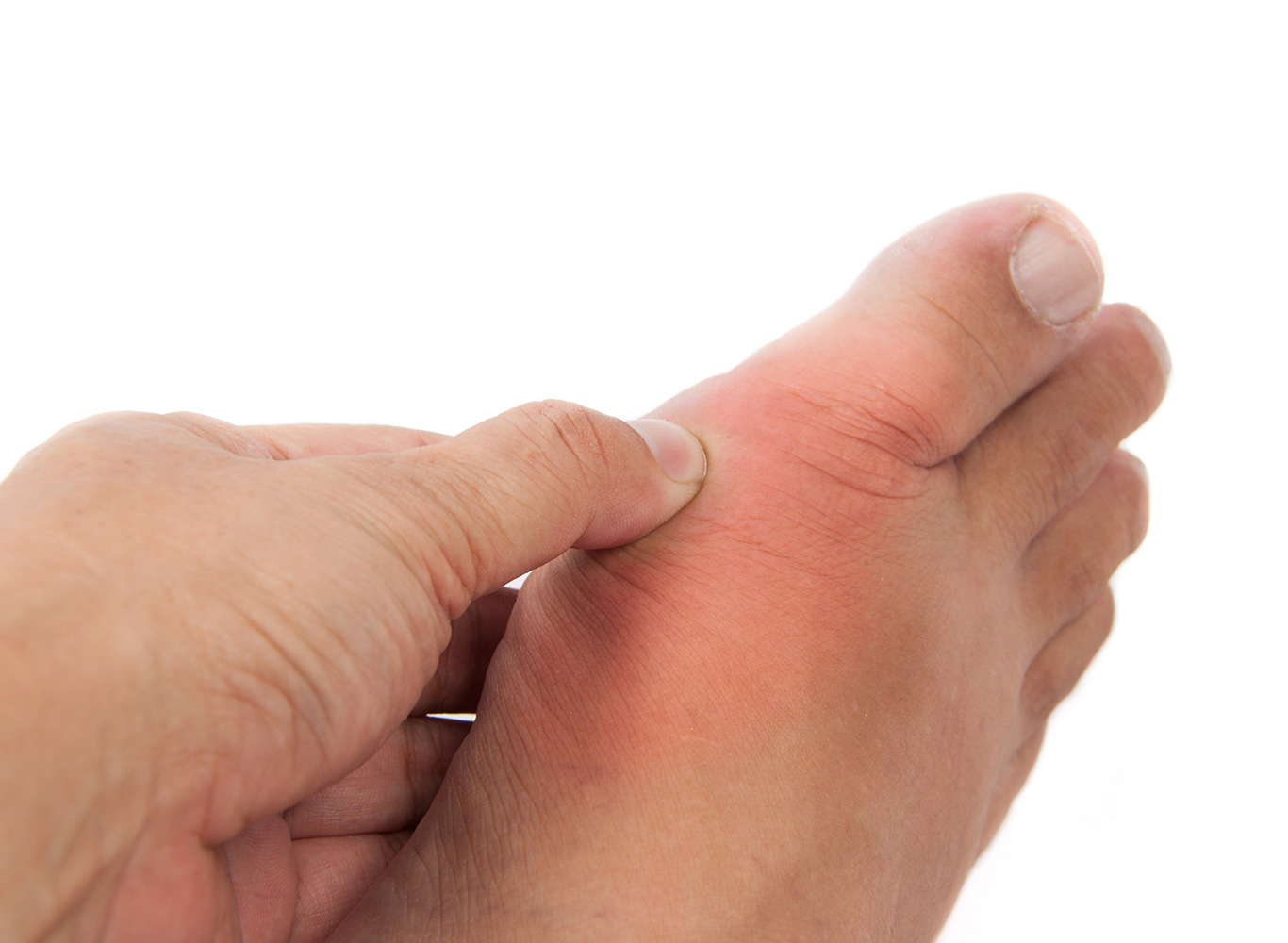
Gout is a type of arthritis that causes sudden joint inflammation, usually in a single joint. Severe gout can sometimes affect many joints at once. This is known as polyarticular gout.
Contents
Causes
Gout is caused by too much uric acid in the bloodstream and accumulation of uric acid crystals in tissues of the body. Uric acid crystal deposits in the joint cause inflammation of the joint leading to pain, redness, heat, and swelling. Uric acid is normally found in the body as a byproduct of the way the body breaks down certain proteins called purines. Causes of an elevated blood uric acid level (hyperuricemia) include genetics, obesity, certain medications such as diuretics (water pills), and chronic decreased kidney function.
Symptoms
The first symptom of gouty arthritis is typically the sudden onset of a hot, red, swollen, stiff, painful joint. The most common joint involved is in the foot at the base of the big toe where swelling can be associated with severe tenderness, but almost any joint can be involved (for example, knee, ankle, and small joints of the hands). In some people, the acute pain is so intense that even a bed sheet on the toe causes severe pain. Acute gouty arthritis at the base of the big toe is referred to as podagra.
Even without treatment, the first attacks stop spontaneously, typically within one to two weeks. While the pain and swelling completely go away, gouty arthritis commonly returns in the same joint or in another joint.
With time, attacks of gouty arthritis can occur more frequently and may last longer. While the first attacks usually involve only one or two joints, multiple joints can be involved simultaneously over time. It is important to note that unrecognizable (subclinical), potentially damaging inflammation in joints can occur between attacks of obvious flares of gouty arthritis.
Kidney stones are more frequent in people with gout.
Uric acid crystals can form outside joints. Collections of these crystals, complications known as tophi, can occur in the earlobe, elbow, and Achilles tendon (back of the ankle), or in other tissues. Typically, these tophi are not painful. However, tophi can be a valuable clue for the diagnosis as the crystals that form them can be removed with a small needle for diagnosis by microscopic examination. Microscopic evaluation of a tophus reveals uric acid crystals.
Treatment
One treatment for active gout flares is colchicine. This medicine can be effective if given early in the attack. However, colchicine can cause nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and other side effects. Side effects may be less frequent with low doses. Patients with kidney or liver disease, or who take drugs that interact (interfere) with colchicine, must take lower doses or use other medicines. Colchicine also has an important role in preventing gout attacks (see below).
Nonsteroidal anti‐inflammatory drugs – commonly called NSAIDs – are aspirin‐like medications that can decrease inflammation and pain in joints and other tissues. NSAIDs, such as indomethacin (Indocin) and naproxen (Naprosyn), have become the treatment choice for most acute attacks of gout. There is no proof that any one NSAID is better than others. High doses of short‐acting NSAIDs give the fastest relief of symptoms. These medicines may cause stomach upset, ulcers or diarrhea, but they are well tolerated by most people when used for the short term. Some people cannot take NSAIDs because of health conditions such as ulcer disease or impaired kidney function or the use of blood thinners. The fact sheet on NSAIDs lists the types of patients who cannot take NSAIDs.
In patients with chronic undertreated gout crystals can be found in uric acid deposits (called tophi) that can damage joints & can appear under the skin. Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, methylprednisolone, and triamcinolone, are useful options for patients who cannot take NSAIDs. Given orally (by mouth) or by injection (shot) into the muscle, these medicines can be very effective in treating gout attacks. If only one or two joints are involved, your doctor can inject a corticosteroid directly into your joint.
Health care providers may prescribe anakinra (Kineret), an “interleukin 1 beta antagonist,” for very severe attacks of gout. Though this rheumatoid arthritis drug is not approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), for gout treatment, it can quickly relieve gout symptoms for some patients.
Natural Remedies
Some home remedies may help ease gout pain and reduce flares. Cherry products such as whole cherries or unsweetened cherry juice may reduce gout flares. A glass of skim milk daily may also help to lower uric acid over time. During an attack, rest the affected joint and apply ice packs or cold compresses (cloths soaked in ice water and wrung out) to that spot.
Cherries
Whether sweet or sour, cherries have been known to be extremely effective in treating gout and lowering uric acid due to their high antioxidant properties. In one study conducted with 600 people suffering from gout, it was concluded that eating half a cup serving of cherries daily (10-12 cherries) resulted in a 35% reduced risk of a successive gout attack. For those eating 2 or even 3 servings in a day, their risk dropped to 50%!
Lemon Juice
Another natural home remedy that helps alkalize your body thus reducing uric acid in the blood, is drinking lemon juice. Many gout sufferers squeeze half a lemon in a glass of 8 oz. of water and drink it up to three times a day. Others will combine it with ½ a teaspoon of baking soda. Remember lemon juice is also high in vitamin C which also helps gout.
Epsom Salt
There is no better topical treatment to treat a gout attack than epsom salt, widely used by many to relax muscles, aches and pains. The presence of magnesium which is an alkaline minreal in epsom salt also helps to treat gout. Before taking a bath, simply add 1 to 2 cups of Epsom salt in your bath and soak your entire body or affected joint, for at least 30 minutes.
Ginger Root
The anti-inflammatory properties present in ginger root can be very helpful in relieving pain and inflammation. There are many ways to use ginger root in the treatment of gout.
Bananas
Bananas are also very effective in treating gout. The high potassium content in bananas will help convert uric acid crystals into liquid form that will be flushed out of the body later through urination. Bananas also contain moderate amounts of vitamin C, which can be very effective in managing swelling and pain.
Cold Water
Placing the affected area in cold water will reduce swelling as well as pain. When you have gout, do not use ice directly on the skin; it can damage the skin and make your condition worse.
