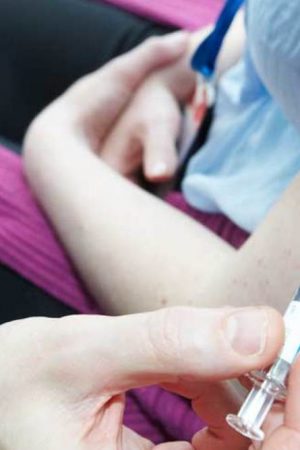
Genital warts are flesh-colored or gray growths found in the genital area and anal region in both men and women. Most people with genital warts are between the ages of 17-33 years. Genital warts are highly contagious. There is high risk of getting the infection from a single sexual contact with someone who has genital warts. In children younger than three years of age, genital warts are thought to be transmitted by nonsexual methods such as direct manual contact. Nevertheless, the presence of genital warts in children should raise the suspicion for sexual abuse. Up to 20% of people with genital warts will have other sexually transmitted diseases (STDs).
Causes
There are over 100 types of human papillomaviruses (HPVs) that infect humans. Of these, more than 40 types can infect the genital tract and anus (anogenital tract) of men and women. Sometimes, they cause genital lesions known as condylomata acuminata or venereal warts. A subgroup of the HPVs that infect the anogenital tract can lead to precancerous changes in the uterine cervix and cervical cancer. HPV infection is also associated with the development of other anogenital cancers. The HPV types that cause cervical cancer have also been linked with both anal and penile cancer in men as well as a subgroup of head and neck cancers in both women and men. Genital warts and HPV infection are transmitted primarily by sexual intimacy, and the risk of infection increases as the number of sexual partner’s increases.
The most common HPV types that infect the anogenital tract are HPV types 6, 11, 16, and 18 (HPV-6, HPV-11, HPV-16, and HPV-18), although other HPV types can also cause infection. Among these, HPV-6 and HPV-11 are most commonly associated with benign lesions such as genital warts are termed “low-risk” HPV types. In contrast, HPV-16 and HPV-18 are the types found most commonly in cervical and anogenital cancers as well as severe dysplasia of the cervix. These belong to the so-called “high-risk” group of HPVs.
Other HPV types infect the skin and cause common warts elsewhere on the body. Some types of HPVs (for example, HPV 5 and 8) frequently cause skin cancers in people who have a condition known as epidermodysplasia verruciformis (EV).
Symptoms
Genital warts appear as raised, flesh-colored lumps or bumps. They may also have a corrugated (cauliflower-like) appearance. They may appear anywhere on body surfaces that are exposed in sexual contact, including the vulva, vagina, cervix, or groin in women and the penis, scrotum, thigh, or groin in males. Size of the warts may vary, and multiple warts may be present at the same time.
In many cases genital warts do not cause any symptoms, but they are sometimes associated with itching, burning, or tenderness. They may result in localized irritation, depending upon their anatomic location. Women who have genital warts inside the vagina may experience symptoms such as bleeding following sexual intercourse or an abnormal vaginal discharge. Rarely, bleeding or urinary obstruction may occur if the wart involves the urethral opening.
Remedies
It may be necessary for you to visit your doctor for treatment for genital warts. You may also want to treat your genital warts at home. Read on to learn about natural home remedies that may help treat genital warts.
Green tea
Green tea has been found to be effective against genital warts. The green tea is concentrated into a compound in an ointment called sinecatechins (Veregen), which is available by prescription.
You can also purchase green tea extract over the counter and use at home by adding a drop or two to coconut oil and applying to the warts.
Apple cider vinegar
Apple cider vinegar may treat genital warts at home. It’s similar to prescription medications that use acidic ingredients to kill off the virus.
You can soak a Q-tip, cotton ball, or gauze in apple cider vinegar and apply it to the warts.
Dietary and lifestyle support
Having genital warts puts a strain on your body. It can be difficult for your body to deal with any other health problems along with the warts. To help your body heal faster, you should cut out any immune stressors like smoking or a diet that is heavy in processed or unhealthy foods.
Witch Hazel
Witch hazel is a fine herb to cure genital warts. The astringent nature of witch hazel makes it a perfect remedy for warts as it makes the undesirable tissues shrink and eventually fall off. Witch hazel inhibits the growth of genital warts by cutting off the blood supply to these tissues.
Tea Tree Oil
Tea tree oil has excellent antiseptic, anti-viral and anti-fungal properties. When you use tea tree oil to get rid of genital warts, you save the surrounding skin too as it just target the warts and nothing else. However, this oil is so strong that it cannot be applied in pure form which may cause skin irritation. Therefore, you need to dilute this oil with a carrier oil before applying on your genital warts.
Genital Wart Advice
HPV or Human Papilloma Virus belongs to a group of viruses that affect the skin and mucous membranes of human beings. It can be easily spread by skin to skin contact. The common treatment for this virus has not been found yet and it is not possible to get rid of the virus completely. The aim of treatment is to improve the immune system of the individual. Curing hpv, also called human papilloma virus or venereal wart, can only be achieved through strengthening the body’s resistant system.
Person suffering from the disease should maintain a healthy lifestyle. To live clean and strengthen immune system are very important. Living with HPV is much easier if you have a healthy body. This prevents the warts from recurring. Intake of vegetables especially Cruciferous vegetables which includes cabbage, brussels sprouts, kale, broccoli and citrus fruits should be increased with minimizing intake of sugars, caffine and refined foods. Herbs such as Echinacea, Phyllanthus emblica, Hyperisince Mysorense are known to boost immunity. Most plants of the Hypericum family have also been studied to have anti-viral effects.